简介
SpringSecurity
官网:https://spring.io/projects/spring-security
身份认证(authentication)
授权(authorization)
防御常见攻击(protection against common attacks)
入门案例
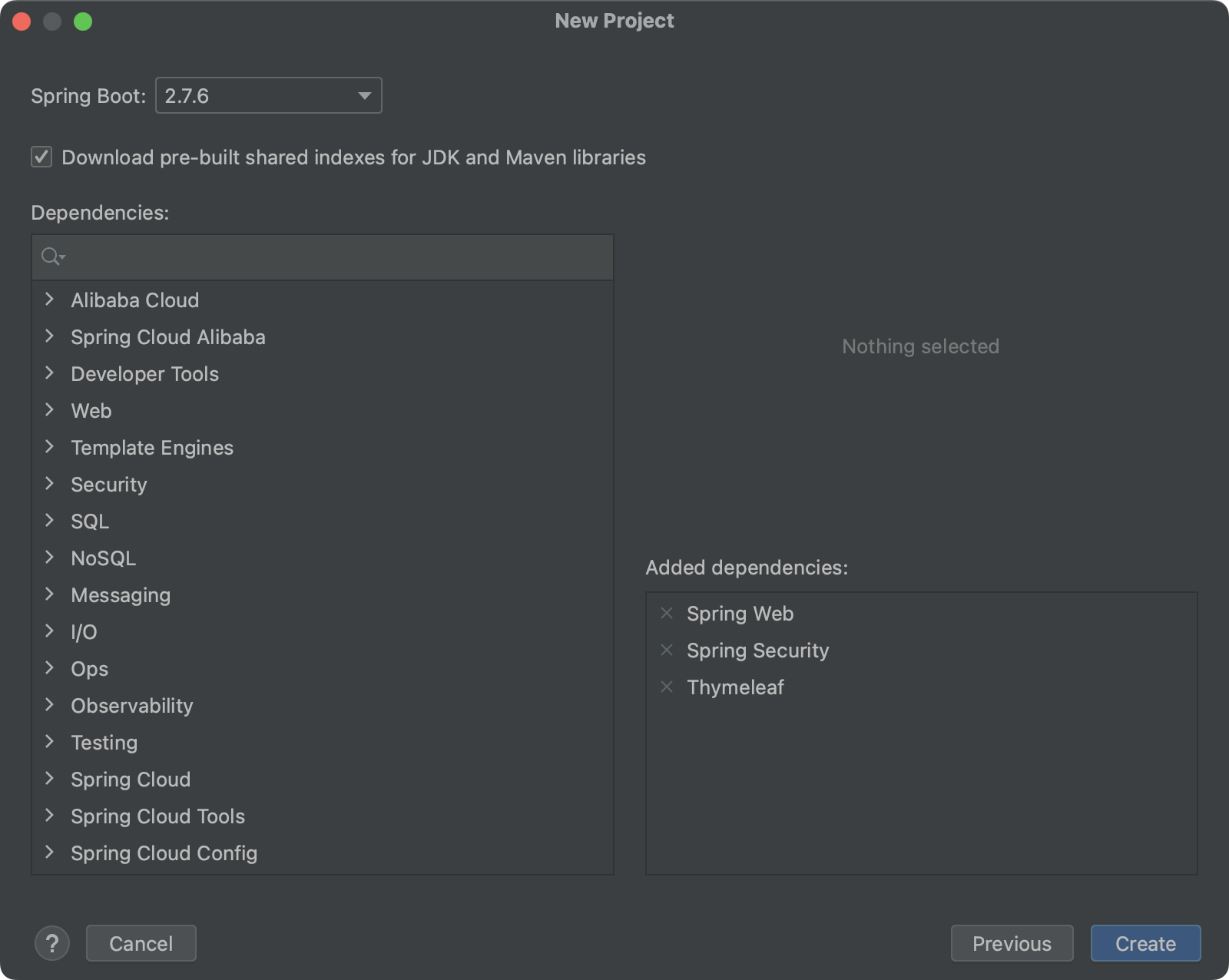
创建SpringBoot项目
我们基于Spring Initializr创建项目,具体过程可以参考《21.SpringBoot [1/3]》 。
需要添加三个依赖:Spring Web、SpringSecurity和Thymeleaf(非必需,仅本文演示需要)。
代码结构
IndexController.java:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.kakawanyifan.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;@Controller public class IndexController @GetMapping ("/" ) public String index () return "index" ; } }
在路径resources/templates下新建index.html:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <html xmlns:th ="https://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head > <title > Hello Security!</title > </head > <body > <h1 > Hello Security</h1 > <a th:href ="@{/logout}" > Log Out</a > </body > </html >
效果
我们启动项目,运行日志如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 【部分运行结果略】 Using generated security password: 3b370801-c87d-43d9-961d-5b9743b5643e This generated password is for development use only. Your security configuration must be updated before running your application in production. 2024-03-24 09:16:59.519 INFO 1890 --- [ main] o.s.s.web.DefaultSecurityFilterChain : Will secure any request with [org.springframework.security.web.session.DisableEncodeUrlFilter@53ac845a, org.springframework.security.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter@5136207f, org.springframework.security.web.context.SecurityContextPersistenceFilter@2c708440, org.springframework.security.web.header.HeaderWriterFilter@cc239ba, org.springframework.security.web.csrf.CsrfFilter@234a8f27, org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutFilter@748e9b20, org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter@35835e65, org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter@3a2b2322, org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter@26a4551a, org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationFilter@4992613f, org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.RequestCacheAwareFilter@6cf31447, org.springframework.security.web.servletapi.SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter@66e8997c, org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AnonymousAuthenticationFilter@3fdecce, org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionManagementFilter@69d6a7cd, org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter@68dcfd52, org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor@17740dae] 2024-03-24 09:16:59.567 INFO 1890 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path '' 2024-03-24 09:16:59.576 INFO 1890 --- [ main] com.kakawanyifan.Application : Started Application in 1.665 seconds (JVM running for 2.33) 2024-03-24 09:17:07.329 INFO 1890 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring DispatcherServlet 'dispatcherServlet' 2024-03-24 09:17:07.329 INFO 1890 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServlet' 2024-03-24 09:17:07.330 INFO 1890 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 1 ms
然后我们在浏览器中访问:http://localhost:8080/ http://localhost:8080/login
用户名user,密码在上文的日志中有Using generated security password: 3b370801-c87d-43d9-961d-5b9743b5643e。
我们也可以将用户名、密码配置在SpringBoot的配置文件中,在application.properties中配置自定义用户名和密码
1 2 spring.security.user.name =user spring.security.user.password =123
自定义配置
基于内存的用户认证
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package com.kakawanyifan.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;import org.springframework.security.provisioning.UserDetailsManager;@Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig @Bean public UserDetailsService userDetailsService () UserDetailsManager userDetailsManager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(); userDetailsManager.createUser( User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder() .username("usr" ) .password("pwd" ) .roles("USER" ) .build() ); return userDetailsManager; } }
解释说明:
UserDetailsManager接口用来管理用户信息,InMemoryUserDetailsManager是UserDetailsManager的一个实现,用来管理基于内存的用户信息。上文我们在application.properties配置的用户名和密码会失效。
基于数据库的用户认证
准备工作
SQL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 CREATE DATABASE `security-demo` ;USE `security-demo` ;CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY , `username` VARCHAR (50 ) DEFAULT NULL , `password` VARCHAR (500 ) DEFAULT NULL , `enabled` BOOLEAN NOT NULL ); CREATE UNIQUE INDEX `user_username_uindex` ON `user` (`username` );INSERT INTO `user` (`username` , `password` , `enabled` )VALUES ('admin' , '{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW' , TRUE ), ('Helen' , '{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW' , TRUE ), ('Tom' , '{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW' , TRUE );
引入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 8.0.30</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.baomidou</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 3.5.4.1</version > <exclusions > <exclusion > <groupId > org.mybatis</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring</artifactId > </exclusion > </exclusions > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring</artifactId > <version > 3.0.3</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > </dependency >
配置数据源
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 spring.datasource.driver-class-name =com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security-demo spring.datasource.username =【用户名】 spring.datasource.password =【密码】 mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl =org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl mybatis-plus.mapper-locations =classpath*:mapper/*.xml mybatis-plus.type-aliases-package =com.kakawanyifan.entity
实体类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package com.kakawanyifan.entity;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;import lombok.Data;@Data public class User @TableId (value = "id" , type = IdType.AUTO) private Integer id; private String username; private String password; private Boolean enabled; }
Mapper
接口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 package com.kakawanyifan.mapper;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;import com.kakawanyifan.entity.User;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;@Mapper public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper <User > }
resources/mapper/UserMapper.xml:
1 2 3 4 5 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="com.atguigu.securitydemo.mapper.UserMapper" > </mapper >
Service
接口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 package com.kakawanyifan.service;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;import com.kakawanyifan.entity.User;public interface UserService extends IService <User > }
实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.kakawanyifan.service.impl;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;import com.kakawanyifan.entity.User;import com.kakawanyifan.mapper.UserMapper;import com.kakawanyifan.service.UserService;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl <UserMapper , User > implements UserService }
Controller
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package com.kakawanyifan.controller;import com.kakawanyifan.entity.User;import com.kakawanyifan.service.UserService;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import javax.annotation.Resource;import java.util.List;@RestController @RequestMapping ("/user" )public class UserController @Resource public UserService userService; @GetMapping ("/list" ) public List<User> getList () return userService.list(); } }
测试
我们访问http://localhost:8080/user/list,输入用户名和密码,会得到如下结果。
DBUserDetailsManager
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 package com.kakawanyifan.config;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;import com.kakawanyifan.entity.User;import com.kakawanyifan.mapper.UserMapper;import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsPasswordService;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;import org.springframework.security.provisioning.UserDetailsManager;import javax.annotation.Resource;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;public class DBUserDetailsManager implements UserDetailsManager , UserDetailsPasswordService @Resource private UserMapper userMapper; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername (String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.eq("username" , username); User user = userMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper); if (user == null ) { throw new UsernameNotFoundException(username); } else { Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>(); return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User( user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), user.getEnabled(), true , true , true , authorities); } } @Override public UserDetails updatePassword (UserDetails user, String newPassword) return null ; } @Override public void createUser (UserDetails user) } @Override public void updateUser (UserDetails user) } @Override public void deleteUser (String username) } @Override public void changePassword (String oldPassword, String newPassword) } @Override public boolean userExists (String username) return false ; } }
WebSecurityConfig
修改WebSecurityConfig中的userDetailsService方法如下
1 2 3 4 5 @Bean public UserDetailsService userDetailsService () DBUserDetailsManager manager = new DBUserDetailsManager(); return manager; }
注意:我们也可以直接在DBUserDetailsManager类上添加@Component注解。
然后我们输入用户名admin、密码password,进行验证登录。
添加用户功能
Controller
在UserController中添加方法:
1 2 3 4 @PostMapping ("/add" )public void add (@RequestBody User user) userService.saveUserDetails(user); }
Service
在UserService接口中添加方法saveUserDetails:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package com.kakawanyifan.service;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;import com.kakawanyifan.entity.User;public interface UserService extends IService <User > void saveUserDetails (User user) }
在UserServiceImpl实现中添加方法saveUserDetails:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 package com.kakawanyifan.service.impl;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;import com.kakawanyifan.config.DBUserDetailsManager;import com.kakawanyifan.entity.User;import com.kakawanyifan.mapper.UserMapper;import com.kakawanyifan.service.UserService;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import javax.annotation.Resource;import java.util.ArrayList;@Service public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl <UserMapper , User > implements UserService @Resource private DBUserDetailsManager dbUserDetailsManager; @Override public void saveUserDetails (User user) UserDetails userDetails = org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User .withDefaultPasswordEncoder() .username(user.getUsername()) .password(user.getPassword()) .authorities(new ArrayList<>()) .build(); dbUserDetailsManager.createUser(userDetails); } }
DBUserDetailsManager
在DBUserDetailsManager中添加方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Override public void createUser (UserDetails user) User u = new User(); u.setUsername(user.getUsername()); u.setPassword(user.getPassword()); u.setEnabled(true ); userMapper.insert(u); }
使用Swagger测试
在pom.xml中添加配置:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.github.xiaoymin</groupId > <artifactId > knife4j-openapi3-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 4.4.0</version > </dependency >
Swagger测试地址:http://localhost:8080/doc.html
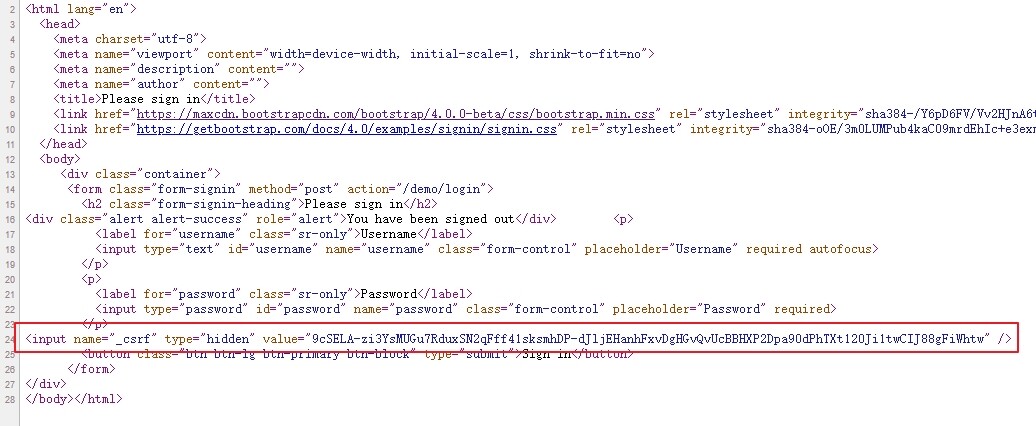
关闭csrf攻击防御
我们通过Sawgger保存,可能会失败。
因为,默认情况下SpringSecurity开启了csrf攻击防御的功能,这要求请求参数中必须有一个隐藏的_csrf字段,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package com.kakawanyifan.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;import static org.springframework.security.config.Customizer.withDefaults;@Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig @Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http .authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize.anyRequest().authenticated()) .formLogin(withDefaults()) .httpBasic(withDefaults()); http.csrf((csrf) -> { csrf.disable(); }); return http.build(); } }
解释说明:SecurityFilterChain filterChain方法默认也会有。在本文,我们再写一遍,然后关闭csrf攻击防御。
1 2 3 http.csrf((csrf) -> { csrf.disable(); });
密码加密算法
密码加密方式
明文密码
Hash算法PasswordEncoder接口用于对密码进行单向转换,从而将密码安全地存储。对密码单向转换需要用到哈希算法,例如MD5、SHA-256、SHA-512等,哈希算法是单向的,只能加密,不能解密。数据库中存储的是单向转换后的密码,SpringSecurity在进行用户身份验证时需要将用户输入的密码进行单向转换,然后与数据库的密码进行比较。暴力破解的方式猜测密码。
彩虹表彩虹表,进行查找。LM、NTLM、MD5、SHA1、MYSQLSHA1、HALFLMCHALL、NTLMCHALL、ORACLE-SYSTEM、MD5-HALF。
加盐密码
自适应单向函数故意占用资源(故意使用大量的CPU、内存或其他资源)。自适应单向函数允许配置一个"工作因子",随着硬件的改进而增加。bcrypt(默认)、PBKDF2、scrypt和argon2。
密码加密测试
在测试类中编写一个测试方法。示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 package com.kakawanyifan;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;import org.springframework.util.Assert;@SpringBootTest class ApplicationTests @Test void contextLoads () } @Test void testPassword () PasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(4 ); String result = encoder.encode("password" ); System.out.println(result); Assert.isTrue(encoder.matches("password" , result), "密码不一致" ); } }
运行结果:
1 $2a$04$naNIaGNnpPyMUhvr1S.Pg.XKVsWEChbzg/jNtSCxujyyrS5Sf5lTi
这个运行结果和我们在数据库中保存的运行结果,存在差异。在数据库中,我们保存如下。有前缀{bcrypt}。
1 {bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW
{bcrypt}用于标识密码的加密方式:在做密码比对的时候会用到,在做密码升级的时候也会用到。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 package org.springframework.security.crypto.password;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map; 【部分代码略】 public class DelegatingPasswordEncoder implements PasswordEncoder 【部分代码略】 @Override public boolean matches (CharSequence rawPassword, String prefixEncodedPassword) if (rawPassword == null && prefixEncodedPassword == null ) { return true ; } String id = extractId(prefixEncodedPassword); PasswordEncoder delegate = this .idToPasswordEncoder.get(id); if (delegate == null ) { return this .defaultPasswordEncoderForMatches.matches(rawPassword, prefixEncodedPassword); } String encodedPassword = extractEncodedPassword(prefixEncodedPassword); return delegate.matches(rawPassword, encodedPassword); } @Override public boolean upgradeEncoding (String prefixEncodedPassword) String id = extractId(prefixEncodedPassword); if (!this .idForEncode.equalsIgnoreCase(id)) { return true ; } else { String encodedPassword = extractEncodedPassword(prefixEncodedPassword); return this .idToPasswordEncoder.get(id).upgradeEncoding(encodedPassword); } } }
自定义登录页面
创建登录Controller
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package com.kakawanyifan.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;@Controller public class LoginController @GetMapping ("/login" ) public String login () return "login" ; } }
创建登录页面
resources/templates/login.html:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <!DOCTYPE html > <html xmlns:th ="https://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head > <title > 登录</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 登录</h1 > <div th:if ="${param.error}" > 错误的用户名和密码.</div > <form th:action ="@{/login}" method ="post" > <div > <input type ="text" name ="username" placeholder ="用户名" /> </div > <div > <input type ="password" name ="password" placeholder ="密码" /> </div > <input type ="submit" value ="登录" /> </form > </body > </html >
配置SecurityFilterChain
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 package com.kakawanyifan.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;import static org.springframework.security.config.Customizer.withDefaults;@Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig @Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http .authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize.anyRequest().authenticated()) .formLogin( form -> { form .loginPage("/login" ).permitAll() .failureUrl("/login?error" ); } ) .httpBasic(withDefaults()); http.csrf((csrf) -> { csrf.disable(); }); return http.build(); } }
重点关注:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 .formLogin( form -> { form .loginPage("/login" ).permitAll() .failureUrl("/login?error" ); } )
自定义字段名
表单的字段名是username和password,如果需要修改可以添加如下两行
1 2 .usernameParameter("uid" ) .passwordParameter("pwd" )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 .formLogin( form -> { form .loginPage("/login" ).permitAll() .usernameParameter("uid" ) .passwordParameter("pwd" ) .failureUrl("/login?error" ); } )
前后端分离
认证过程
认证过程如下:
登录成功后调用:AuthenticationSuccessHandler
登录失败后调用:AuthenticationFailureHandler
认证成功的响应
成功结果处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package com.kakawanyifan.handler;import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler;import javax.servlet.ServletException;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.HashMap;public class MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler @Override public void onAuthenticationSuccess (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal(); HashMap result = new HashMap(); result.put("code" , 0 ); result.put("message" , "登录成功" ); result.put("data" , principal); String json = JSON.toJSONString(result); response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8" ); response.getWriter().println(json); } }
需要添加依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba.fastjson2</groupId > <artifactId > fastjson2</artifactId > <version > 2.0.37</version > </dependency >
SecurityFilterChain配置
添加如下代码:
1 2 .successHandler(new MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler())
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 package com.kakawanyifan.config;import com.kakawanyifan.handler.MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;import static org.springframework.security.config.Customizer.withDefaults;@Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig @Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http .authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize.anyRequest().authenticated()) .formLogin( form -> { form .loginPage("/login" ).permitAll() .usernameParameter("uid" ) .passwordParameter("pwd" ) .failureUrl("/login?error" ) .successHandler(new MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler()); } ) .httpBasic(withDefaults()); http.csrf((csrf) -> { csrf.disable(); }); return http.build(); } }
认证失败响应
失败结果处理
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package com.kakawanyifan.handler;import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler;import javax.servlet.ServletException;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.HashMap;public class MyAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler @Override public void onAuthenticationFailure (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException String localizedMessage = exception.getLocalizedMessage(); HashMap result = new HashMap(); result.put("code" , -1 ); result.put("message" , localizedMessage); String json = JSON.toJSONString(result); response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8" ); response.getWriter().println(json); } }
SecurityFilterChain配置
添加如下代码:
1 2 .failureHandler(new MyAuthenticationFailureHandler())
注销响应
注销结果处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package com.kakawanyifan.handler;import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutSuccessHandler;import javax.servlet.ServletException;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.HashMap;public class MyLogoutSuccessHandler implements LogoutSuccessHandler @Override public void onLogoutSuccess (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException HashMap result = new HashMap(); result.put("code" , 0 ); result.put("message" , "注销成功" ); String json = JSON.toJSONString(result); response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8" ); response.getWriter().println(json); } }
SecurityFilterChain配置
添加如下代码:
1 2 3 4 http.logout(logout -> { logout.logoutSuccessHandler(new MyLogoutSuccessHandler()); });
请求未认证的接口
实现AuthenticationEntryPoint接口
当访问一个需要认证之后才能访问的接口的时候,SpringSecurity会使用AuthenticationEntryPoint将用户请求跳转到登录页面,要求用户提供登录凭证。
这里我们也希望系统"返回JSON结果",因此我们定义类实现AuthenticationEntryPoint接口。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package com.kakawanyifan.handler;import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;import org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint;import javax.servlet.ServletException;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.HashMap;public class MyAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint @Override public void commence (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException HashMap result = new HashMap(); result.put("code" , -1 ); result.put("message" , "需要登录" ); String json = JSON.toJSONString(result); response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8" ); response.getWriter().println(json); } }
SecurityFilterChain配置
添加如下代码:
1 2 3 4 http.exceptionHandling(exception -> { exception.authenticationEntryPoint(new MyAuthenticationEntryPoint()); });
跨域
跨域全称是跨域资源共享(Cross-Origin Resources Sharing,CORS),它是浏览器的保护机制,只允许网页请求统一域名下的服务。协议、域名、端口号都要保持一致,如果有一项不同,那么就是跨域请求。
在前后端分离的项目中,需要解决跨域的问题。
在SpringSecurity中解决跨域很简单,在配置文件中添加如下配置即可:
1 2 http.cors(withDefaults());
身份认证
用户认证信息
基本概念
SecurityContextHolder用于管理当前线程的安全上下文,存储已认证用户的详细信息。
其中包含了SecurityContext对象,该对象包含了Authentication对象。
Authentication对象表示用户的身份验证信息,包括Principal(用户的身份标识)和Credential(用户的凭证信息)。
例子
这些信息,我们在上文"前后端分离"部分,都已经用过了。
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 package com.kakawanyifan.controller;import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;@RestController public class IndexController @GetMapping ("/" ) public Map index () System.out.println("index controller" ); SecurityContext securityContext = SecurityContextHolder.getContext(); Authentication authentication = securityContext.getAuthentication(); String username = authentication.getName(); Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal(); Object credentials = authentication.getCredentials(); Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities(); System.out.println(username); System.out.println(principal); System.out.println(credentials); System.out.println(authorities); HashMap result = new HashMap(); result.put("code" , 0 ); result.put("data" , username); return result; } }
运行结果:
1 2 3 4 5 index controller admin org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User [Username=admin, Password=[PROTECTED], Enabled=true, AccountNonExpired=true, credentialsNonExpired=true, AccountNonLocked=true, Granted Authorities=[]] null []
会话并发处理
需求
后登录的账号会使先登录的账号失效
实现处理器接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package com.kakawanyifan.strategy;import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;import org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionInformationExpiredEvent;import org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionInformationExpiredStrategy;import javax.servlet.ServletException;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.HashMap;public class MySessionInformationExpiredStrategy implements SessionInformationExpiredStrategy @Override public void onExpiredSessionDetected (SessionInformationExpiredEvent event) throws IOException, ServletException HashMap result = new HashMap(); result.put("code" , -1 ); result.put("message" , "该账号已从其他设备登录" ); String json = JSON.toJSONString(result); HttpServletResponse response = event.getResponse(); response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8" ); response.getWriter().println(json); } }
SecurityFilterChain配置
添加如下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 http.sessionManagement(session -> { session .maximumSessions(1 ) .expiredSessionStrategy(new MySessionInformationExpiredStrategy()); });
授权
分类
按照授权方式分类,有:
用户-权限-资源USER_LIST权限的用户可以访问/user/list接口,具有USER_ADD权限的用户可以访问/user/add接口。
用户-角色-资源/user/**路径下的资源。
用户-角色-权限-资源
按照实现方法分类,有:
基于request的授权
基于方法的授权
基于request的授权
用户-权限-资源
需求背景
具有USER_LIST权限的用户可以访问/user/list接口,具有USER_ADD权限的用户可以访问/user/add接口。
配置权限
添加如下部分:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 http.authorizeRequests( authorize -> authorize .antMatchers("/user/list" ).hasAuthority("USER_LIST" ) .antMatchers("/user/add" ).hasAuthority("USER_ADD" ) .anyRequest() .authenticated() );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 package com.kakawanyifan.config;import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;import com.kakawanyifan.handler.MyAuthenticationEntryPoint;import com.kakawanyifan.handler.MyAuthenticationFailureHandler;import com.kakawanyifan.handler.MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler;import com.kakawanyifan.handler.MyLogoutSuccessHandler;import com.kakawanyifan.strategy.MySessionInformationExpiredStrategy;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;import java.util.HashMap;import static org.springframework.security.config.Customizer.withDefaults;@Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig @Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http.authorizeRequests( authorize -> authorize .antMatchers("/user/list" ).hasAuthority("USER_LIST" ) .antMatchers("/user/add" ).hasAuthority("USER_ADD" ) .anyRequest() .authenticated() ); http.formLogin( form -> { form .loginPage("/login" ).permitAll() .failureUrl("/login?error" ) .successHandler(new MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler()) .failureHandler(new MyAuthenticationFailureHandler()); } ) .httpBasic(withDefaults()); http.csrf((csrf) -> { csrf.disable(); }); http.logout(logout -> { logout.logoutSuccessHandler(new MyLogoutSuccessHandler()); }); http.exceptionHandling(exception -> { exception.authenticationEntryPoint(new MyAuthenticationEntryPoint()); }); http.cors(withDefaults()); http.sessionManagement(session -> { session .maximumSessions(1 ) .expiredSessionStrategy(new MySessionInformationExpiredStrategy()); }); http.exceptionHandling(exception -> { exception.authenticationEntryPoint(new MyAuthenticationEntryPoint()); exception.accessDeniedHandler((request, response, e)->{ HashMap result = new HashMap(); result.put("code" , -1 ); result.put("message" , "没有权限" ); String json = JSON.toJSONString(result); response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8" ); response.getWriter().println(json); }); }); return http.build(); } }
授予权限
修改DBUserDetailsManager中的loadUserByUsername方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>(); authorities.add(new GrantedAuthority() { @Override public String getAuthority () return "USER_ADD" ; } });
我们也采取如下写法:
1 2 3 Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>(); authorities.add(()->"USER_LIST" ); authorities.add(()->"USER_ADD" );
请求未授权的接口
添加如下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 http.exceptionHandling(exception -> { exception.authenticationEntryPoint(new MyAuthenticationEntryPoint()); exception.accessDeniedHandler((request, response, e)->{ HashMap result = new HashMap(); result.put("code" , -1 ); result.put("message" , "没有权限" ); String json = JSON.toJSONString(result); response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8" ); response.getWriter().println(json); }); });
用户-角色-资源
需求背景
角色为ADMIN的用户才可以访问/user/**路径下的资源。
配置角色
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 http.authorizeRequests( authorize -> authorize .antMatchers("/user/**" ).hasRole("ADMIN" ) .anyRequest() .authenticated() );
授予角色
添加如下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 return org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User .withUsername(user.getUsername()) .password(user.getPassword()) .roles("ADMIN" ) .build();
并删除如下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User( user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), user.getEnabled(), true , true , true , authorities);
用户-角色-权限-资源
什么是用户-角色-权限-资源
RBAC,Role-Based Access Control,基于角色的访问控制,将用户的权限分配和管理与角色相关联。
数据库设计
一、用户表,包含用户的基本信息,例如用户名、密码和其他身份验证信息。
列名
数据类型
描述
user_id
int
用户ID
username
varchar
用户名
password
varchar
密码
email
varchar
电子邮件地址
…
…
…
二、角色表,存储所有可能的角色及其描述。
列名
数据类型
描述
role_id
int
角色ID
role_name
varchar
角色名称
description
varchar
角色描述
…
…
…
三、权限表,定义系统中所有可能的权限。
列名
数据类型
描述
permission_id
int
权限ID
permission_name
varchar
权限名称
description
varchar
权限描述
…
…
…
四、用户角色关联表,将用户与角色关联起来。
列名
数据类型
描述
user_role_id
int
用户角色关联ID
user_id
int
用户ID
role_id
int
角色ID
…
…
…
五、角色权限关联表,将角色与权限关联起来。
列名
数据类型
描述
role_permission_id
int
角色权限关联ID
role_id
int
角色ID
permission_id
int
权限ID
…
…
…
在这个设计方案中,用户可以被分配一个或多个角色,而每个角色又可以具有一个或多个权限。通过对用户角色关联和角色权限关联表进行操作,可以实现灵活的权限管理和访问控制。
当用户尝试访问系统资源时,系统可以根据用户的角色和权限决定是否允许访问。这样的设计方案使得权限管理更加简单和可维护,因为只需调整角色和权限的分配即可,而不需要针对每个用户进行单独的设置。
代码实现
那么,怎么实现呢?
和"用户-权限-资源"没有区别,只是在获取用户权限的时候,需要关联查询一下。
基于方法的授权
开启方法授权
在配置文件中添加如下注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableMethodSecurity;【部分代码略】 @EnableMethodSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig 【部分代码略】 }
给用户授予角色和权限
修改DBUserDetailsManager中的loadUserByUsername方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 return org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User .withUsername(user.getUsername()) .password(user.getPassword()) .authorities("USER_ADD" , "USER_UPDATE" ) .build();
注意:
.authorities("USER_ADD", "USER_UPDATE"),如果我们想添加多个权限,不能写两遍.authorities(),应该传入一个String... authorities。.authorities不但会覆盖前一个.authorities,还会覆盖.roles。即两个不能同时使用。
常用授权注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 package com.kakawanyifan.controller;import com.kakawanyifan.entity.User;import com.kakawanyifan.service.UserService;import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;import javax.annotation.Resource;import java.util.List;@RestController @RequestMapping ("/user" )public class UserController @Resource public UserService userService; @PreAuthorize ("hasRole('ADMIN') and authentication.name == 'admim'" ) @GetMapping ("/list" ) public List<User> getList () return userService.list(); } @PreAuthorize ("hasAuthority('USER_ADD')" ) @PostMapping ("/add" ) public void add (@RequestBody User user) userService.saveUserDetails(user); } }
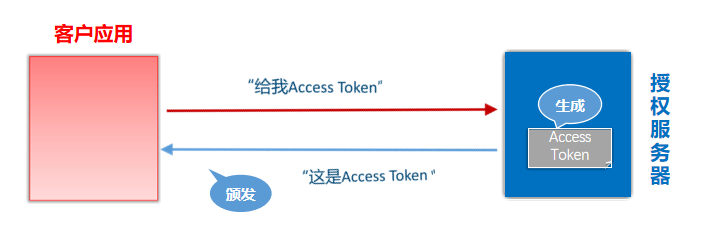
OAuth2
简介
什么是OAuth2
“Auth"表示"Authorization”,授权。
连在一起,就是"开放授权",即一种开放授权协议。
(“2”,表示第二个版本。)
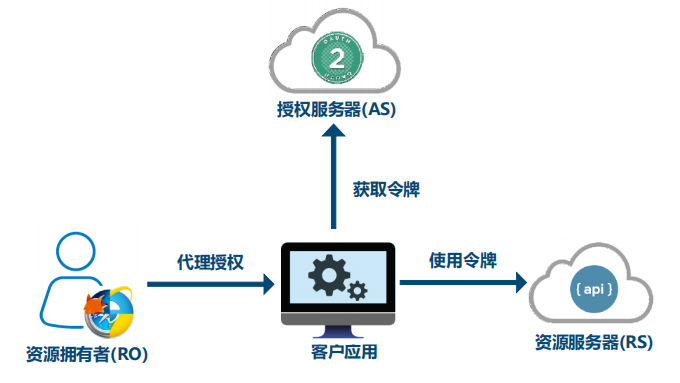
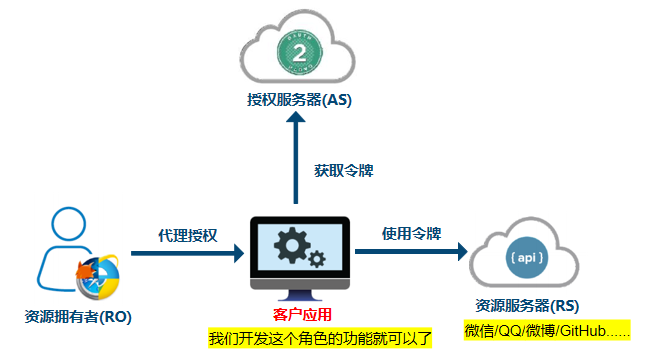
OAuth2的角色
OAuth2协议包含以下角色:
资源所有者(Resource Owner)
客户应用(Client)
资源服务器(Resource Server)
授权服务器(Authorization Server)
使用场景
开放系统间授权
社交登录
开放API
企业内部应用认证授权
SSO,Single Sign On,单点登录。
IAM,Identity and Access Management,身份识别与访问管理。
现代微服务安全
OAuth2的四种授权模式
授权码(authorization-code)
隐藏式(implicit)
密码式(password)
客户端凭证(client credentials)
授权码
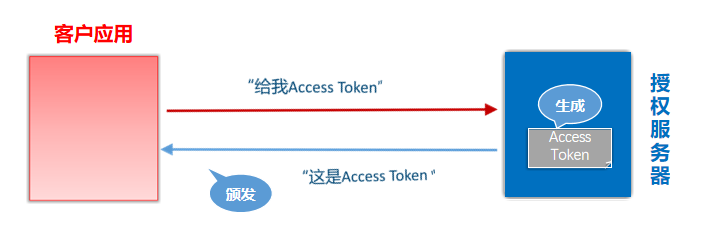
授权码,authorization code,指的是第三方应用先申请一个授权码,然后再用该码获取令牌。
这种方式是最常用,最复杂,也是最安全的,它适用于那些有后端的Web应用。授权码通过前端传送,令牌则是储存在后端,而且所有与资源服务器的通信都在后端完成。这样的前后端分离,可以避免令牌泄漏。
隐藏式
隐藏式,implicit,也叫简化模式,有些Web应用是纯前端应用,没有后端。这时就不能用上面的方式了,必须将令牌储存在前端。
这种方式没有授权码这个中间步骤,所以称为隐藏式。这种方式把令牌直接传给前端,是很不安全的。因此,只能用于一些安全要求不高的场景,并且令牌的有效期必须非常短,通常就是会话期间(session)有效,浏览器关掉,令牌就失效了。
密码式
密码式,Resource Owner Password Credentials,如果我们高度信任某个应用,也可以把用户把用户名和密码,直接告诉该应用。该应用就使用你的密码,申请令牌。
这种方式需要用户给出自己的用户名/密码,显然风险很大,因此只适用于其他授权方式都无法采用的情况,而且必须是用户高度信任的应用。
凭证式
凭证式,client credentials,也叫客户端模式,适用于没有前端的命令行应用,即在命令行下请求令牌。
这种方式给出的令牌,是针对第三方应用的,而不是针对用户的,即有可能多个用户共享同一个令牌。
授权类型的选择
Spring中的OAuth2
相关角色
在上文,我们说OAuth2有四个角色
资源所有者(Resource Owner)
客户应用(Client)
资源服务器(Resource Server)
授权服务器(Authorization Server)
在Spring中角色划分如下:
SpringSecurity
客户应用(OAuth2 Client),OAuth2客户端功能中包含OAuth2 Login。
资源服务器(OAuth2 Resource Server)
Spring:
相关依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-oauth2-authorization-server</artifactId > </dependency >
授权登录的实现思路
使用OAuth2 Login。
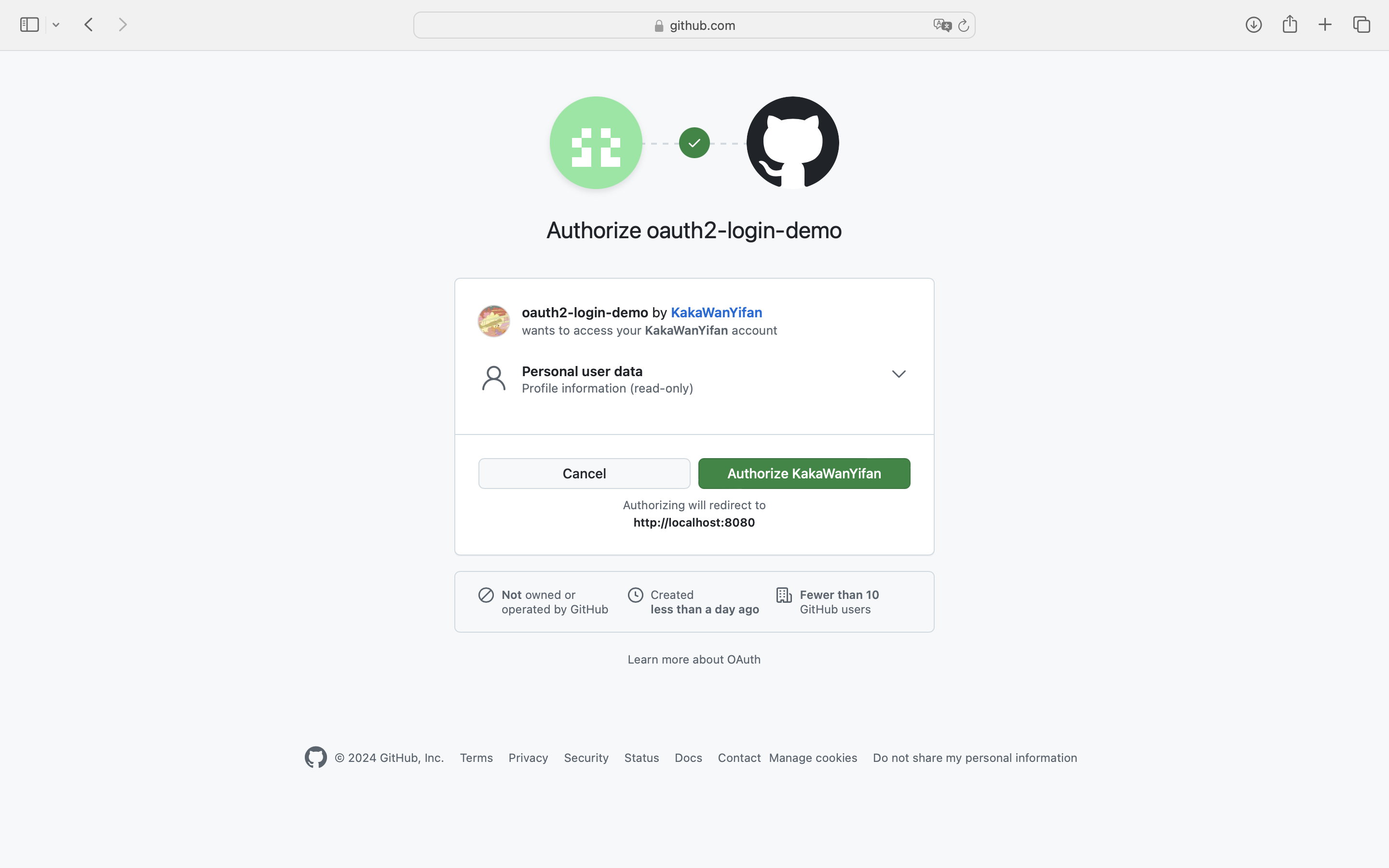
案例(GiuHub社交登录)
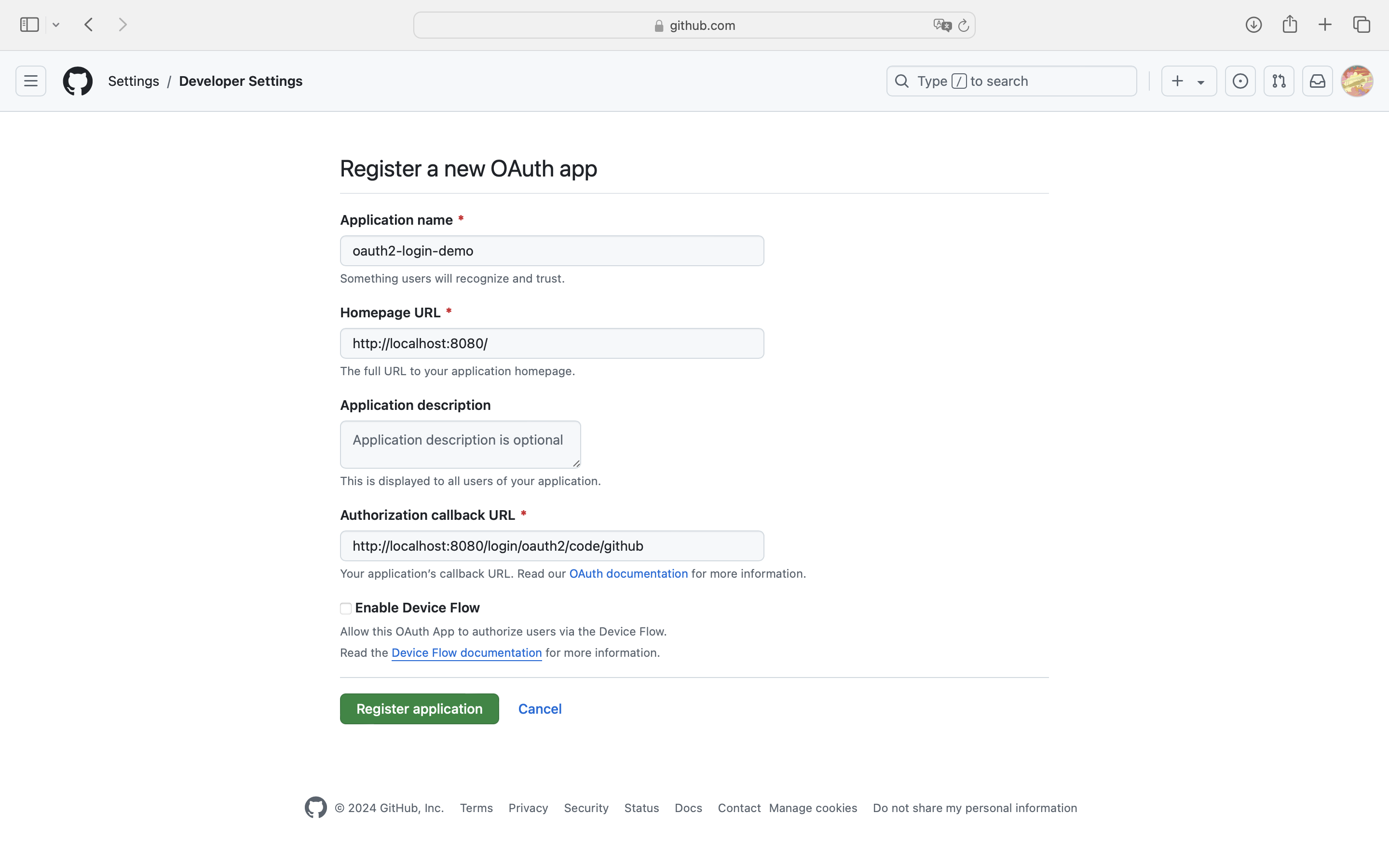
创建应用
登录GitHub,在开发者设置中找到OAuth Apps,创建一个application,为客户应用创建访问GitHub的凭据。https://github.com/settings/developers
默认的重定向URI模板为
1 {baseUrl}/login/oauth2/code/{registrationId}
registrationId是ClientRegistration的唯一标识符。
例如,在我们本机开发中,填写如下:
获取应用程序ID,生成应用程序密钥。
创建测试项目
创建一个SpringBoot项目,创建时引入如下依赖
Spring Web
Thymeleaf(非必需,仅本文演示需要)
SpringSecurity
Auth2 Client
配置OAuth客户端属性
application.properties:
1 2 3 spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.github.client-id =【Client ID】 spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.github.client-secret =【Client secrets】
Controller
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 package com.kakawanyifan.controller;import org.springframework.security.core.annotation.AuthenticationPrincipal;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.OAuth2AuthorizedClient;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.annotation.RegisteredOAuth2AuthorizedClient;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.user.OAuth2User;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;@Controller public class IndexController @GetMapping ("/" ) public String index ( Model model, @RegisteredOAuth2AuthorizedClient OAuth2AuthorizedClient authorizedClient, @AuthenticationPrincipal OAuth2User oauth2User) model.addAttribute("userName" , oauth2User.getName()); model.addAttribute("clientName" , authorizedClient.getClientRegistration().getClientName()); model.addAttribute("userAttributes" , oauth2User.getAttributes()); return "index" ; } }
HTML
templates/index.html:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 <!DOCTYPE html > <html xmlns ="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th ="https://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec ="https://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5" > <head > <title > SpringSecurity - OAuth 2.0 Login</title > <meta charset ="utf-8" /> </head > <body > <div style ="float: right" th:fragment ="logout" sec:authorize ="isAuthenticated()" > <div style ="float:left" > <span style ="font-weight:bold" > User: </span > <span sec:authentication ="name" > </span > </div > <div style ="float:none" > </div > <div style ="float:right" > <form action ="#" th:action ="@{/logout}" method ="post" > <input type ="submit" value ="Logout" /> </form > </div > </div > <h1 > OAuth 2.0 Login with SpringSecurity</h1 > <div > You are successfully logged in <span style ="font-weight:bold" th:text ="${userName}" > </span > via the OAuth 2.0 Client <span style ="font-weight:bold" th:text ="${clientName}" > </span > </div > <div > </div > <div > <span style ="font-weight:bold" > User Attributes:</span > <ul > <li th:each ="userAttribute : ${userAttributes}" > <span style ="font-weight:bold" th:text ="${userAttribute.key}" > </span > : <span th:text ="${userAttribute.value}" > </span > </li > </ul > </div > </body > </html >
效果
然后我们启动程序并访问http://localhost:8080,浏览器将被重定向到默认的自动生成的登录页面。
点击GitHub链接,浏览器将被重定向到GitHub进行身份验证。
使用GitHub账户凭据进行身份验证后,用户会看到授权页面,询问用户是否允许或拒绝客户应用访问GitHub上的用户数据。点击允许以授权OAuth客户端访问用户的基本个人资料信息。
此时,OAuth客户端访问GitHub的获取用户信息的接口获取基本个人资料信息,并建立一个已认证的会话。
CommonOAuth2Provider
CommonOAuth2Provider是一个预定义的通用OAuth2Provider,为一些知名资源服务API提供商(如Google、GitHub、Facebook)预定义了一组默认的属性。
例如,授权URI、令牌URI和用户信息URI通常不经常变化。因此,提供默认值以减少所需的配置。
org.springframework.security.config.oauth2.client.CommonOAuth2Provider:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 package org.springframework.security.config.oauth2.client;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.registration.ClientRegistration;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.registration.ClientRegistration.Builder;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.AuthorizationGrantType;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.ClientAuthenticationMethod;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.oidc.IdTokenClaimNames;public enum CommonOAuth2Provider { GOOGLE { @Override public Builder getBuilder (String registrationId) ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBuilder(registrationId, ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL); builder.scope("openid" , "profile" , "email" ); builder.authorizationUri("https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/auth" ); builder.tokenUri("https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token" ); builder.jwkSetUri("https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/certs" ); builder.issuerUri("https://accounts.google.com" ); builder.userInfoUri("https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/userinfo" ); builder.userNameAttributeName(IdTokenClaimNames.SUB); builder.clientName("Google" ); return builder; } }, GITHUB { @Override public Builder getBuilder (String registrationId) ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBuilder(registrationId, ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL); builder.scope("read:user" ); builder.authorizationUri("https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize" ); builder.tokenUri("https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token" ); builder.userInfoUri("https://api.github.com/user" ); builder.userNameAttributeName("id" ); builder.clientName("GitHub" ); return builder; } }, FACEBOOK { @Override public Builder getBuilder (String registrationId) ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBuilder(registrationId, ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_POST, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL); builder.scope("public_profile" , "email" ); builder.authorizationUri("https://www.facebook.com/v2.8/dialog/oauth" ); builder.tokenUri("https://graph.facebook.com/v2.8/oauth/access_token" ); builder.userInfoUri("https://graph.facebook.com/me?fields=id,name,email" ); builder.userNameAttributeName("id" ); builder.clientName("Facebook" ); return builder; } }, OKTA { @Override public Builder getBuilder (String registrationId) ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBuilder(registrationId, ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL); builder.scope("openid" , "profile" , "email" ); builder.userNameAttributeName(IdTokenClaimNames.SUB); builder.clientName("Okta" ); return builder; } }; private static final String DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL = "{baseUrl}/{action}/oauth2/code/{registrationId}" ; protected final ClientRegistration.Builder getBuilder (String registrationId, ClientAuthenticationMethod method, String redirectUri) ClientRegistration.Builder builder = ClientRegistration.withRegistrationId(registrationId); builder.clientAuthenticationMethod(method); builder.authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE); builder.redirectUri(redirectUri); return builder; } public abstract ClientRegistration.Builder getBuilder (String registrationId) ; }
JWT
概述
什么是JWT
官网地址: https://jwt.io
JWT,Json Web Token,通过JSON的形式传递web应用中的令牌,用于在各方之间安全的将信息作为JSON对象传输,在传输过程中还可以完成数据加密、签名等相关处理。
作用
授权
信息交换
session的缺点
关于session,可以参考《13.Servlet、Filter和Listener》
session是保存在服务器端的内存当中,随着登录用户的不断增多,服务器端需要的内存会比较大,造成成本增加。 如果是分布式项目还要涉及到分布式session方案的设计。 由于session是通过cookie传输sessionid来进行工作的,如果cookie被截取,用户很容易遭受到跨站请求伪造的攻击。 在前后端分离的情况下,前端的请求会经过很多的中间件,每次请求转发都会到服务器验证,造成服务器压力增大。
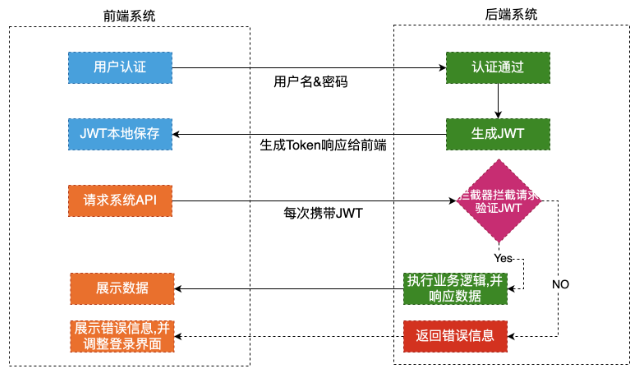
认证流程
前端通过Web表单将自己的用户名和密码发送到后端的接口,这个过程一般是HTTP-POST请求。
后端核对用户名和密码成功后,将用户的id等其他信息作为JWT Payload,将其与头部分别进行Base64编码拼接后签名,形成一个JWT(Token)。形成的JWT就是一个形同xxx.yyy.zzz的字符串。
后端将JWT字符串作为登录成功的返回结果返回给前端。前端可以将返回的结果保存在localStorage或sessionStorage上,退出登录时前端删除保存的JWT即可。
前端在每次请求时将JWT放入HTTP Header中的Authorization位。
后端检查是否存在,如存在验证JWT的有效性。例如,检查签名是否正确;检查Token是否过期;检查Token的接收方是否是自己(可选)。
验证通过后,后端使用JWT中包含的用户信息进行其他逻辑操作,返回相应结果。
优势:
简洁:可以通过URL,POST参数或者在HTTP header发送,因为数据量小,传输速度也很快。
自包含:负载中包含了所有用户所需要的信息,避免了多次查询数据库。
因为Token是以JSON加密的形式保存在客户端的,所以JWT是跨语言的,原则上任何web形式都支持。
不需要在服务端保存会话信息,特别适用于分布式微服务。
JWT的结构
JWT主要由三部分组成:
标头(Header)
有效载荷(Payload)
签名(Signature)。
功能
定义了令牌的类型(即JWT)及所使用的签名算法,如HMAC、SHA256或RSA。
示例
1 2 3 4 { "alg" : "HS256" , "typ" : "JWT" }
处理
这部分信息经过Base64编码后成为JWT的第一部分。
有效载荷(Payload)
功能
存储声明(claims),声明是关于实体(通常是用户)及其他数据的信息片段。
示例
1 2 3 4 5 { "sub" : "123456" , "name" : "Augus" , "admin" : true }
处理
同样,这部分也需Base64编码,并构成JWT的第二部分。
签名(Signature)
功能
确保消息在传输过程中的完整性,防止被篡改。
生成方式
使用编码后的标头+有效载荷加上密钥,通过指定的签名算法计算得出。
重要性
服务器端会验证签名以确保JWT没有被修改过。如果JWT的内容被改动,那么新的签名与原始签名不匹配,从而可以检测到篡改行为。
整体结构
整个JWT字符串由上述三个部分经Base64编码后连接而成,中间用点号.分隔。格式为xxxxx.yyyyy.zzzzz,其中xxxxx是标头,yyyyy是有效载荷,而zzzzz是对前两部分进行签名的结果。
实践
JJWT
JJWT是一个提供端到端的JWT创建和验证的Java库。
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > io.jsonwebtoken</groupId > <artifactId > jjwt</artifactId > <version > 0.9.1</version > </dependency >
加密和解密
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 package com.kakawanyifan;import io.jsonwebtoken.*;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;import java.security.Key;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;@SpringBootTest class DemoApplicationTests @Test public void testJJWT () Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("type" , 1 ); String payload = "{\"user_id\":\"13579\", \"expire_time\":\"2024-03-11 10:00:00\"}" ; Key KEY = new SecretKeySpec("kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan" .getBytes(), SignatureAlgorithm.HS512.getJcaName()); String compact = Jwts.builder().setHeader(map).setPayload(payload).signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS512, KEY).compact(); System.out.println("jwt key:" + new String(KEY.getEncoded())); System.out.println("jwt payload:" + payload); System.out.println("jwt encoded:" + compact); Jws<Claims> claimsJws = Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(KEY).parseClaimsJws(compact); JwsHeader header = claimsJws.getHeader(); Claims body = claimsJws.getBody(); System.out.println("jwt header:" + header); System.out.println("jwt body:" + body); System.out.println("jwt body user-id:" + body.get("user_id" , String.class )) ; } }
运行结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 jwt key:kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan-kakawanyifan jwt payload:{"user_id":"13579", "expire_time":"2024-03-11 10:00:00"} jwt encoded:eyJ0eXBlIjoxLCJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9.eyJ1c2VyX2lkIjoiMTM1NzkiLCAiZXhwaXJlX3RpbWUiOiIyMDI0LTAzLTExIDEwOjAwOjAwIn0.-_AAJoEcw40_eQcXZ-lRQNKGwa-r97Zh4mhB8Gd4Uxr-KDPaZRVtnhHqRofs_jrnm3ag7AZZctiINoLkYyuUWA jwt header:{type=1, alg=HS512} jwt body:{user_id=13579, expire_time=2024-03-11 10:00:00} jwt body user-id:13579