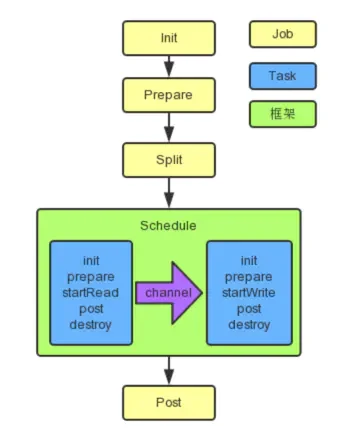
整体流程
程序入口
我们从datax.py开始。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 if __name__ == "__main__" : printCopyright() parser = getOptionParser() options, args = parser.parse_args(sys.argv[1 :]) if options.reader is not None and options.writer is not None : generateJobConfigTemplate(options.reader, options.writer) sys.exit(RET_STATE['OK' ]) if len(args) != 1 : parser.print_help() sys.exit(RET_STATE['FAIL' ]) startCommand = buildStartCommand(options, args) child_process = subprocess.Popen(startCommand, shell=True ) register_signal() (stdout, stderr) = child_process.communicate() sys.exit(child_process.returncode)
其中getOptionParser(),作用是解析参数,上一章我们传入的-r、-w以及--jvm,都是通过这里进行解析。该方法具体我们不讨论,重点关注buildStartCommand方法。
1 2 3 4 5 def buildStartCommand (options, args) :【解析参数,代码略】 return Template(ENGINE_COMMAND).substitute(**commandMap)
在该方法的最后有这么一段return Template(ENGINE_COMMAND).substitute(**commandMap)。
ENGINE_COMMAND的定义如下:
1 ENGINE_COMMAND = "java -server ${jvm} %s -classpath %s ${params} com.alibaba.datax.core.Engine -mode ${mode} -jobid ${jobid} -job ${job}" % (DEFAULT_PROPERTY_CONF, CLASS_PATH)
如此,找到了程序的主入口,在com.alibaba.datax.core.Engine这个类中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception int exitCode = 0 ; try { Engine.entry(args); } catch (Throwable e) { exitCode = 1 ; LOG.error("\n\n经DataX智能分析,该任务最可能的错误原因是:\n" + ExceptionTracker.trace(e)); if (e instanceof DataXException) { DataXException tempException = (DataXException) e; ErrorCode errorCode = tempException.getErrorCode(); if (errorCode instanceof FrameworkErrorCode) { FrameworkErrorCode tempErrorCode = (FrameworkErrorCode) errorCode; exitCode = tempErrorCode.toExitValue(); } } System.exit(exitCode); } System.exit(exitCode); }
点进Engine.entry(args)
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void entry (final String[] args) throws Throwable 【生成配置,代码略】 engine.start(configuration); }
我们点进engine.start(configuration);。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public void start (Configuration allConf) 【部分代码略】 if (isJob) { allConf.set(CoreConstant.DATAX_CORE_CONTAINER_JOB_MODE, RUNTIME_MODE); container = new JobContainer(allConf); instanceId = allConf.getLong( CoreConstant.DATAX_CORE_CONTAINER_JOB_ID, 0 ); } else { container = new TaskGroupContainer(allConf); instanceId = allConf.getLong( CoreConstant.DATAX_CORE_CONTAINER_JOB_ID); taskGroupId = allConf.getInt( CoreConstant.DATAX_CORE_CONTAINER_TASKGROUP_ID); channelNumber = allConf.getInt( CoreConstant.DATAX_CORE_CONTAINER_TASKGROUP_CHANNEL); } 【部分代码略】 container.start(); }
注意container.start();,container可能在两个地方进行定义:
container = new JobContainer(allConf);container = new TaskGroupContainer(allConf);
先来看JobContainer,我们关注其start方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 @Override public void start () LOG.info("DataX jobContainer starts job." ); boolean hasException = false ; boolean isDryRun = false ; try { this .startTimeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); isDryRun = configuration.getBool(CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_SETTING_DRYRUN, false ); if (isDryRun) { LOG.info("jobContainer starts to do preCheck ..." ); this .preCheck(); } else { userConf = configuration.clone(); LOG.debug("jobContainer starts to do preHandle ..." ); this .preHandle(); LOG.debug("jobContainer starts to do init ..." ); this .init(); LOG.info("jobContainer starts to do prepare ..." ); this .prepare(); LOG.info("jobContainer starts to do split ..." ); this .totalStage = this .split(); LOG.info("jobContainer starts to do schedule ..." ); this .schedule(); LOG.debug("jobContainer starts to do post ..." ); this .post(); LOG.debug("jobContainer starts to do postHandle ..." ); this .postHandle(); LOG.info("DataX jobId [{}] completed successfully." , this .jobId); this .invokeHooks(); } } catch (Throwable e) { 【部分代码略】 } finally { 【部分代码略】 } }
注意this.init();、this.prepare();、this.totalStage = this.split();、this.schedule();、this.post();,和本章开篇的图对上了。
Task切分逻辑
我们点进this.totalStage = this.split();,查看Task切分逻辑。
切分方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 private int split () this .adjustChannelNumber(); if (this .needChannelNumber <= 0 ) { this .needChannelNumber = 1 ; } List<Configuration> readerTaskConfigs = this .doReaderSplit(this .needChannelNumber); int taskNumber = readerTaskConfigs.size(); List<Configuration> writerTaskConfigs = this .doWriterSplit(taskNumber); List<Configuration> transformerList = this .configuration.getListConfiguration(CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_CONTENT_TRANSFORMER); LOG.debug("transformer configuration: " + JSON.toJSONString(transformerList)); List<Configuration> contentConfig = mergeReaderAndWriterTaskConfigs( readerTaskConfigs, writerTaskConfigs, transformerList); LOG.debug("contentConfig configuration: " + JSON.toJSONString(contentConfig)); this .configuration.set(CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_CONTENT, contentConfig); return contentConfig.size(); }
先来看this.adjustChannelNumber();,点进去。
并发数的确定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 private void adjustChannelNumber () int needChannelNumberByByte = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int needChannelNumberByRecord = Integer.MAX_VALUE; boolean isByteLimit = (this .configuration.getInt( CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_SETTING_SPEED_BYTE, 0 ) > 0 ); if (isByteLimit) { long globalLimitedByteSpeed = this .configuration.getInt( CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_SETTING_SPEED_BYTE, 10 * 1024 * 1024 ); Long channelLimitedByteSpeed = this .configuration .getLong(CoreConstant.DATAX_CORE_TRANSPORT_CHANNEL_SPEED_BYTE); if (channelLimitedByteSpeed == null || channelLimitedByteSpeed <= 0 ) { throw DataXException.asDataXException( FrameworkErrorCode.CONFIG_ERROR, "在有总bps限速条件下,单个channel的bps值不能为空,也不能为非正数" ); } needChannelNumberByByte = (int ) (globalLimitedByteSpeed / channelLimitedByteSpeed); needChannelNumberByByte = needChannelNumberByByte > 0 ? needChannelNumberByByte : 1 ; LOG.info("Job set Max-Byte-Speed to " + globalLimitedByteSpeed + " bytes." ); } boolean isRecordLimit = (this .configuration.getInt( CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_SETTING_SPEED_RECORD, 0 )) > 0 ; if (isRecordLimit) { long globalLimitedRecordSpeed = this .configuration.getInt( CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_SETTING_SPEED_RECORD, 100000 ); Long channelLimitedRecordSpeed = this .configuration.getLong( CoreConstant.DATAX_CORE_TRANSPORT_CHANNEL_SPEED_RECORD); if (channelLimitedRecordSpeed == null || channelLimitedRecordSpeed <= 0 ) { throw DataXException.asDataXException(FrameworkErrorCode.CONFIG_ERROR, "在有总tps限速条件下,单个channel的tps值不能为空,也不能为非正数" ); } needChannelNumberByRecord = (int ) (globalLimitedRecordSpeed / channelLimitedRecordSpeed); needChannelNumberByRecord = needChannelNumberByRecord > 0 ? needChannelNumberByRecord : 1 ; LOG.info("Job set Max-Record-Speed to " + globalLimitedRecordSpeed + " records." ); } this .needChannelNumber = needChannelNumberByByte < needChannelNumberByRecord ? needChannelNumberByByte : needChannelNumberByRecord; if (this .needChannelNumber < Integer.MAX_VALUE) { return ; } boolean isChannelLimit = (this .configuration.getInt( CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_SETTING_SPEED_CHANNEL, 0 ) > 0 ); if (isChannelLimit) { this .needChannelNumber = this .configuration.getInt( CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_SETTING_SPEED_CHANNEL); LOG.info("Job set Channel-Number to " + this .needChannelNumber + " channels." ); return ; } throw DataXException.asDataXException( FrameworkErrorCode.CONFIG_ERROR, "Job运行速度必须设置" ); }
其中:
1 public static final String DATAX_JOB_SETTING_SPEED_BYTE = "job.setting.speed.byte" ;
对应我们JSON的setting.speed.byte
1 public static final String DATAX_JOB_SETTING_SPEED_RECORD = "job.setting.speed.record" ;
对应我们JSON的setting.speed.record
然后,我们看到,在确定needChannelNumberByByte和needChannelNumberByRecord后,会取最小值。this.needChannelNumber < Integer.MAX_VALUE,就return;而needChannelNumber的初始值为:
1 2 int needChannelNumberByByte = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int needChannelNumberByRecord = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
也就是说,只有record和byte都没设置,channel才可能有效,即优先级最低。《1.操作方法》 ,调优部分的讨论。
reader和writer任务数对等
在this.adjustChannelNumber();后,还有两行
1 2 3 4 5 List<Configuration> readerTaskConfigs = this .doReaderSplit(this .needChannelNumber); int taskNumber = readerTaskConfigs.size();List<Configuration> writerTaskConfigs = this .doWriterSplit(taskNumber);
该部分是reader的切分和writer的切分,注意int taskNumber = readerTaskConfigs.size();,也就是说writer的切分参数来自reader。List<Configuration> writerTaskConfigs = this.doWriterSplit(taskNumber);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 private List<Configuration> doWriterSplit (int readerTaskNumber) classLoaderSwapper.setCurrentThreadClassLoader(LoadUtil.getJarLoader( PluginType.WRITER, this .writerPluginName)); List<Configuration> writerSlicesConfigs = this .jobWriter .split(readerTaskNumber); if (writerSlicesConfigs == null || writerSlicesConfigs.size() <= 0 ) { throw DataXException.asDataXException( FrameworkErrorCode.PLUGIN_SPLIT_ERROR, "writer切分的task不能小于等于0" ); } LOG.info("DataX Writer.Job [{}] splits to [{}] tasks." , this .writerPluginName, writerSlicesConfigs.size()); classLoaderSwapper.restoreCurrentThreadClassLoader(); return writerSlicesConfigs; }
再点进List<Configuration> writerSlicesConfigs = this.jobWriter.split(readerTaskNumber);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 package com.alibaba.datax.common.spi; 【部分代码略】 /** * 每个Writer插件需要实现Writer类,并在其内部实现Job、Task两个内部类。 * * * */ public abstract class Writer extends BaseObject { /** * 每个Writer插件必须实现Job内部类 */ public abstract static class Job extends AbstractJobPlugin { /** * 切分任务。<br> * * @param mandatoryNumber * 为了做到Reader、Writer任务数对等,这里要求Writer插件必须按照源端的切分数进行切分。否则框架报错! * * */ public abstract List<Configuration> split(int mandatoryNumber); } 【部分代码略】 }
注意split(int mandatoryNumber);方法的注释。即read和writer的任务数对等,一比一。
调度
看完了this.totalStage = this.split();,我们再点进this.schedule();。
调度方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 private void schedule () 【部分代码略】 List<Configuration> taskGroupConfigs = JobAssignUtil.assignFairly(this .configuration, this .needChannelNumber, channelsPerTaskGroup); LOG.info("Scheduler starts [{}] taskGroups." , taskGroupConfigs.size()); ExecuteMode executeMode = null ; AbstractScheduler scheduler; try { executeMode = ExecuteMode.STANDALONE; scheduler = initStandaloneScheduler(this .configuration); for (Configuration taskGroupConfig : taskGroupConfigs) { taskGroupConfig.set(CoreConstant.DATAX_CORE_CONTAINER_JOB_MODE, executeMode.getValue()); } if (executeMode == ExecuteMode.LOCAL || executeMode == ExecuteMode.DISTRIBUTE) { if (this .jobId <= 0 ) { throw DataXException.asDataXException(FrameworkErrorCode.RUNTIME_ERROR, "在[ local | distribute ]模式下必须设置jobId,并且其值 > 0 ." ); } } LOG.info("Running by {} Mode." , executeMode); this .startTransferTimeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); scheduler.schedule(taskGroupConfigs); this .endTransferTimeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); } catch (Exception e) { LOG.error("运行scheduler 模式[{}]出错." , executeMode); this .endTransferTimeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); throw DataXException.asDataXException( FrameworkErrorCode.RUNTIME_ERROR, e); } this .checkLimit(); }
点进
1 List<Configuration> taskGroupConfigs = JobAssignUtil.assignFairly(this .configuration,this .needChannelNumber, channelsPerTaskGroup);
确定组数和分组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public static List<Configuration> assignFairly (Configuration configuration, int channelNumber, int channelsPerTaskGroup) Validate.isTrue(configuration != null , "框架获得的 Job 不能为 null." ); List<Configuration> contentConfig = configuration.getListConfiguration(CoreConstant.DATAX_JOB_CONTENT); Validate.isTrue(contentConfig.size() > 0 , "框架获得的切分后的 Job 无内容." ); Validate.isTrue(channelNumber > 0 && channelsPerTaskGroup > 0 , "每个channel的平均task数[averTaskPerChannel],channel数目[channelNumber],每个taskGroup的平均channel数[channelsPerTaskGroup]都应该为正数" ); int taskGroupNumber = (int ) Math.ceil(1.0 * channelNumber / channelsPerTaskGroup); Configuration aTaskConfig = contentConfig.get(0 ); String readerResourceMark = aTaskConfig.getString(CoreConstant.JOB_READER_PARAMETER + "." + CommonConstant.LOAD_BALANCE_RESOURCE_MARK); String writerResourceMark = aTaskConfig.getString(CoreConstant.JOB_WRITER_PARAMETER + "." + CommonConstant.LOAD_BALANCE_RESOURCE_MARK); boolean hasLoadBalanceResourceMark = StringUtils.isNotBlank(readerResourceMark) || StringUtils.isNotBlank(writerResourceMark); if (!hasLoadBalanceResourceMark) { for (Configuration conf : contentConfig) { conf.set(CoreConstant.JOB_READER_PARAMETER + "." + CommonConstant.LOAD_BALANCE_RESOURCE_MARK, "aFakeResourceMarkForLoadBalance" ); } Collections.shuffle(contentConfig, new Random(System.currentTimeMillis())); } LinkedHashMap<String, List<Integer>> resourceMarkAndTaskIdMap = parseAndGetResourceMarkAndTaskIdMap(contentConfig); List<Configuration> taskGroupConfig = doAssign(resourceMarkAndTaskIdMap, configuration, taskGroupNumber); adjustChannelNumPerTaskGroup(taskGroupConfig, channelNumber); return taskGroupConfig; }
注意这段代码:
1 int taskGroupNumber = (int ) Math.ceil(1.0 * channelNumber / channelsPerTaskGroup);
这就印证了我们在上一章《1.操作方法》 说的,100个Task、channel数是20,问需要多少个taskGroupNumber,channelsPerTaskGroup默认是5.taskGroupNumber是4。
点进List<Configuration> taskGroupConfig = doAssign(resourceMarkAndTaskIdMap, configuration, taskGroupNumber);
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 private static List<Configuration> doAssign (LinkedHashMap<String, List<Integer>> resourceMarkAndTaskIdMap, Configuration jobConfiguration, int taskGroupNumber) 【部分代码略】 }
该方法的代码略,我们主要看注释。a、b、c,三个库
a 库上有表:0, 1, 2b 库上有表:3, 4c 库上有表:5, 6, 7
然后我们有4个taskGroup,taskGroup-0处理a库的0,taskGroup-1处理b库的3,taskGroup-2处理c库的5,taskGroup-3处理a库的1,以此类推。
这也是,我在上一章《1.操作方法》 说的,100个Task,4个TaskGroup公平分配,不一定第一个TaskGroup就负责25个Task。
此处,源代码存在一个注释错误。b 库上有表:3, 4,而不是a 库上有表:3, 4。
特别的,我们可以再回到调度方法,关注一下这段代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 executeMode = ExecuteMode.STANDALONE; scheduler = initStandaloneScheduler(this .configuration); for (Configuration taskGroupConfig : taskGroupConfigs) { taskGroupConfig.set(CoreConstant.DATAX_CORE_CONTAINER_JOB_MODE, executeMode.getValue()); } if (executeMode == ExecuteMode.LOCAL || executeMode == ExecuteMode.DISTRIBUTE) { if (this .jobId <= 0 ) { throw DataXException.asDataXException(FrameworkErrorCode.RUNTIME_ERROR, "在[ local | distribute ]模式下必须设置jobId,并且其值 > 0 ." ); } }
在executeMode = ExecuteMode.STANDALONE;,已经写死了。if (executeMode == ExecuteMode.LOCAL || executeMode == ExecuteMode.DISTRIBUTE) {,又做判断?
数据传输
调用逻辑
我们可以继续点进JobContainer的schedule()方法的scheduler.schedule(taskGroupConfigs);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public void schedule (List<Configuration> configurations) 【部分代码略】 int totalTasks = calculateTaskCount(configurations); startAllTaskGroup(configurations); 【部分代码略】 }
我们点进startAllTaskGroup(configurations);,是一个抽象方法。找到实现类的方法,是这个
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Override public void startAllTaskGroup (List<Configuration> configurations) this .taskGroupContainerExecutorService = Executors .newFixedThreadPool(configurations.size()); for (Configuration taskGroupConfiguration : configurations) { TaskGroupContainerRunner taskGroupContainerRunner = newTaskGroupContainerRunner(taskGroupConfiguration); this .taskGroupContainerExecutorService.execute(taskGroupContainerRunner); } this .taskGroupContainerExecutorService.shutdown(); }
this.taskGroupContainerExecutorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(configurations.size());是在申请线程池,那么执行的任务是什么呢?
点进TaskGroupContainerRunner,找到run()方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 package com.alibaba.datax.core.taskgroup.runner;【部分代码略】 public class TaskGroupContainerRunner implements Runnable 【部分代码略】 @Override public void run () try { Thread.currentThread().setName( String.format("taskGroup-%d" , this .taskGroupContainer.getTaskGroupId())); this .taskGroupContainer.start(); this .state = State.SUCCEEDED; } catch (Throwable e) { this .state = State.FAILED; throw DataXException.asDataXException( FrameworkErrorCode.RUNTIME_ERROR, e); } } 【部分代码略】 }
点进this.taskGroupContainer.start();。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Override public void start () try { 【部分代码略】 Configuration taskConfigForRun = taskMaxRetryTimes > 1 ? taskConfig.clone() : taskConfig; TaskExecutor taskExecutor = new TaskExecutor(taskConfigForRun, attemptCount); taskStartTimeMap.put(taskId, System.currentTimeMillis()); taskExecutor.doStart(); 【部分代码略】 } catch (Throwable e) { 【部分代码略】 }finally { 【部分代码略】 } }
点进taskExecutor.doStart()。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public void doStart () this .writerThread.start(); if (!this .writerThread.isAlive() || this .taskCommunication.getState() == State.FAILED) { throw DataXException.asDataXException( FrameworkErrorCode.RUNTIME_ERROR, this .taskCommunication.getThrowable()); } this .readerThread.start(); if (!this .readerThread.isAlive() && this .taskCommunication.getState() == State.FAILED) { throw DataXException.asDataXException( FrameworkErrorCode.RUNTIME_ERROR, this .taskCommunication.getThrowable()); } }
以readerThread为例,点击this.readerThread.start();的readerThread,发现其是一个成员变量,是由构造方法进行赋值的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public TaskExecutor (Configuration taskConf, int attemptCount) 【部分代码略】 writerRunner = (WriterRunner) generateRunner(PluginType.WRITER); this .writerThread = new Thread(writerRunner, String.format("%d-%d-%d-writer" , jobId, taskGroupId, this .taskId)); 【部分运行结果略】 readerRunner = (ReaderRunner) generateRunner(PluginType.READER,transformerInfoExecs); this .readerThread = new Thread(readerRunner, String.format("%d-%d-%d-reader" , jobId, taskGroupId, this .taskId)); }
发现writerRunner和readerRunner均来自generateRunner,并进行强制转换。点进ReaderRunner。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 package com.alibaba.datax.core.taskgroup.runner;【部分代码略】 public class ReaderRunner extends AbstractRunner implements Runnable 【部分代码略】 @Override public void run () assert null != this .recordSender; Reader.Task taskReader = (Reader.Task) this .getPlugin(); PerfRecord channelWaitWrite = new PerfRecord(getTaskGroupId(), getTaskId(), PerfRecord.PHASE.WAIT_WRITE_TIME); try { channelWaitWrite.start(); LOG.debug("task reader starts to do init ..." ); PerfRecord initPerfRecord = new PerfRecord(getTaskGroupId(), getTaskId(), PerfRecord.PHASE.READ_TASK_INIT); initPerfRecord.start(); taskReader.init(); initPerfRecord.end(); LOG.debug("task reader starts to do prepare ..." ); PerfRecord preparePerfRecord = new PerfRecord(getTaskGroupId(), getTaskId(), PerfRecord.PHASE.READ_TASK_PREPARE); preparePerfRecord.start(); taskReader.init(); preparePerfRecord.end(); LOG.debug("task reader starts to read ..." ); PerfRecord dataPerfRecord = new PerfRecord(getTaskGroupId(), getTaskId(), PerfRecord.PHASE.READ_TASK_DATA); dataPerfRecord.start(); taskReader.startRead(recordSender); recordSender.terminate(); dataPerfRecord.addCount(CommunicationTool.getTotalReadRecords(super .getRunnerCommunication())); dataPerfRecord.addSize(CommunicationTool.getTotalReadBytes(super .getRunnerCommunication())); dataPerfRecord.end(); LOG.debug("task reader starts to do post ..." ); PerfRecord postPerfRecord = new PerfRecord(getTaskGroupId(), getTaskId(), PerfRecord.PHASE.READ_TASK_POST); postPerfRecord.start(); taskReader.post(); postPerfRecord.end(); } catch (Throwable e) { LOG.error("Reader runner Received Exceptions:" , e); super .markFail(e); } finally { LOG.debug("task reader starts to do destroy ..." ); PerfRecord desPerfRecord = new PerfRecord(getTaskGroupId(), getTaskId(), PerfRecord.PHASE.READ_TASK_DESTROY); desPerfRecord.start(); super .destroy(); desPerfRecord.end(); 【部分代码略】 } } public void shutdown () recordSender.shutdown(); } }
注意看其中的run方法,有子方法taskReader.init();、taskReader.init();、taskReader.startRead(recordSender);、taskReader.post();和super.destroy();。和本章开篇的图"Schedule"部分对上了。
我们重点关注startRead,这是一个抽象方法,实现类有很多。我们以MySQL的为例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Override public void startRead (RecordSender recordSender) int fetchSize = this .readerSliceConfig.getInt(Constant.FETCH_SIZE); this .commonRdbmsReaderTask.startRead(this .readerSliceConfig, recordSender, super .getTaskPluginCollector(), fetchSize); }
点进commonRdbmsReaderTask.startRead
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public void startRead (Configuration readerSliceConfig, RecordSender recordSender, TaskPluginCollector taskPluginCollector, int fetchSize) ResultSet rs = null ; try { while (rs.next()) { rsNextUsedTime += (System.nanoTime() - lastTime); this .transportOneRecord(recordSender, rs, metaData, columnNumber, mandatoryEncoding, taskPluginCollector); lastTime = System.nanoTime(); } }catch (Exception e) { throw RdbmsException.asQueryException(this .dataBaseType, e, querySql, table, username); } finally { DBUtil.closeDBResources(null , conn); } }
点进transportOneRecord。
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 protected Record transportOneRecord (RecordSender recordSender, ResultSet rs, ResultSetMetaData metaData, int columnNumber, String mandatoryEncoding, TaskPluginCollector taskPluginCollector) Record record = buildRecord(recordSender,rs,metaData,columnNumber,mandatoryEncoding,taskPluginCollector); recordSender.sendToWriter(record); return record; }
限速方法
点进sendToWriter。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override public void sendToWriter (Record record) if (shutdown){ throw DataXException.asDataXException(CommonErrorCode.SHUT_DOWN_TASK, "" ); } Validate.notNull(record, "record不能为空." ); if (record.getMemorySize() > this .byteCapacity) { this .pluginCollector.collectDirtyRecord(record, new Exception(String.format("单条记录超过大小限制,当前限制为:%s" , this .byteCapacity))); return ; } boolean isFull = (this .bufferIndex >= this .bufferSize || this .memoryBytes.get() + record.getMemorySize() > this .byteCapacity); if (isFull) { flush(); } this .buffer.add(record); this .bufferIndex++; memoryBytes.addAndGet(record.getMemorySize()); }
点进flush()方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Override public void flush () if (shutdown){ throw DataXException.asDataXException(CommonErrorCode.SHUT_DOWN_TASK, "" ); } this .channel.pushAll(this .buffer); this .buffer.clear(); this .bufferIndex = 0 ; this .memoryBytes.set(0 ); }
点进this.channel.pushAll(this.buffer);。
1 2 3 4 5 6 public void pushAll(final Collection<Record> rs) { Validate.notNull(rs); Validate.noNullElements(rs); this.doPushAll(rs); this.statPush(rs.size(), this.getByteSize(rs)); }
点进this.statPush(rs.size(), this.getByteSize(rs));。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 private void statPush (long recordSize, long byteSize) currentCommunication.increaseCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_SUCCEED_RECORDS, recordSize); currentCommunication.increaseCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_SUCCEED_BYTES, byteSize); currentCommunication.setLongCounter(CommunicationTool.WAIT_READER_TIME, waitReaderTime); currentCommunication.setLongCounter(CommunicationTool.WAIT_WRITER_TIME, waitWriterTime); boolean isChannelByteSpeedLimit = (this .byteSpeed > 0 ); boolean isChannelRecordSpeedLimit = (this .recordSpeed > 0 ); if (!isChannelByteSpeedLimit && !isChannelRecordSpeedLimit) { return ; } long lastTimestamp = lastCommunication.getTimestamp(); long nowTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); long interval = nowTimestamp - lastTimestamp; if (interval - this .flowControlInterval >= 0 ) { long byteLimitSleepTime = 0 ; long recordLimitSleepTime = 0 ; if (isChannelByteSpeedLimit) { long currentByteSpeed = (CommunicationTool.getTotalReadBytes(currentCommunication) - CommunicationTool.getTotalReadBytes(lastCommunication)) * 1000 / interval; if (currentByteSpeed > this .byteSpeed) { byteLimitSleepTime = currentByteSpeed * interval / this .byteSpeed - interval; } } if (isChannelRecordSpeedLimit) { long currentRecordSpeed = (CommunicationTool.getTotalReadRecords(currentCommunication) - CommunicationTool.getTotalReadRecords(lastCommunication)) * 1000 / interval; if (currentRecordSpeed > this .recordSpeed) { recordLimitSleepTime = currentRecordSpeed * interval / this .recordSpeed - interval; } } long sleepTime = byteLimitSleepTime < recordLimitSleepTime ? recordLimitSleepTime : byteLimitSleepTime; if (sleepTime > 0 ) { try { Thread.sleep(sleepTime); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } lastCommunication.setLongCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_SUCCEED_BYTES, currentCommunication.getLongCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_SUCCEED_BYTES)); lastCommunication.setLongCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_FAILED_BYTES, currentCommunication.getLongCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_FAILED_BYTES)); lastCommunication.setLongCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_SUCCEED_RECORDS, currentCommunication.getLongCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_SUCCEED_RECORDS)); lastCommunication.setLongCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_FAILED_RECORDS, currentCommunication.getLongCounter(CommunicationTool.READ_FAILED_RECORDS)); lastCommunication.setTimestamp(nowTimestamp); } }
找到了!
这种通过"Sleep"进行速度控制的方法,还在一个地方有,Kakfa。《消息队列(Kafka与RabbitMQ):Kafka-5.监控、调优和避免消息丢失》 的"Broker调优"的"动态配置"。